rockwell hardness test means|rockwell hardness test explained : purchase The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different . See more WEBFollow @brotheragen on Twitter to see the hottest and most daring brotherhood videos and photos. Join the community of over 200k followers and enjoy the best content of .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web9 de fev. de 2024 · O site 123321bet.com é seguro? Esse site possui selo de segurança https ou SSL, registrado pela empresa DigiCert Inc, com validade até 11/8/2024. O selo .
The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different . See moreThe differential depth hardness measurement was conceived in 1908 by Viennese professor Paul Ludwik in his book Die Kegelprobe (crudely, "the cone test"). The differential-depth method . See more
The Rockwell hardness test can be conducted on several various hardness testers. All testers, however, fall under one of three categories. Bench model hardness testers can be found . See moreThere are several alternative scales, the most commonly used being the "B" and "C" scales. Both express hardness as an arbitrary See more• International (ISO)• US standard (ASTM International) See more• Brinell hardness test• Hardness comparison• Holger F. Struer• Knoop hardness test See more
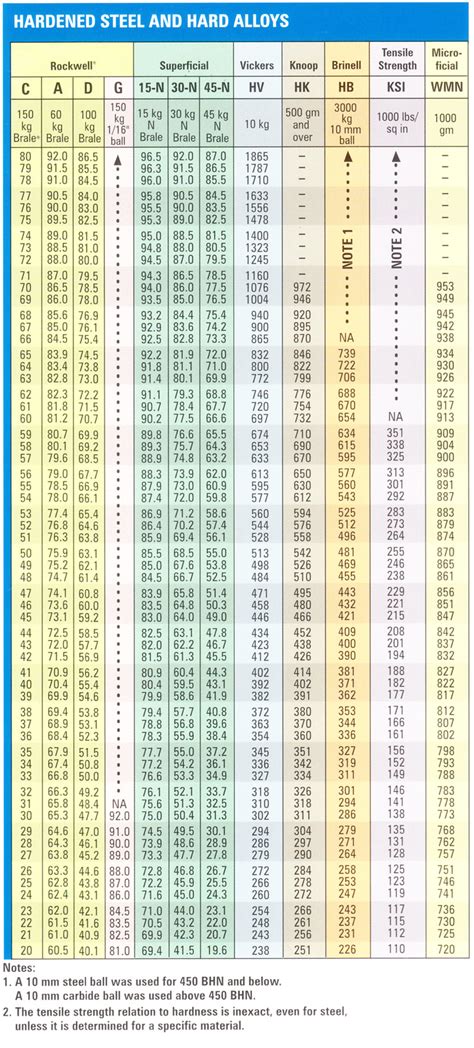
rockwell hardness testing chart
• Video on the Rockwell hardness test• Hardness Conversion Chart• Rockwell to brinell conversion chart• Hardness Conversion Table See more
compression lift gas springs
The scale has different numbers that represent hardness based on the indent's depth caused by the test material's indentation. Let us look at how you can measure and . To accurately express metal hardness, engineers use a standard process called Rockwell testing. In the knife blade manufacturing business, hardness ratings follow a predetermined chart which is commonly called the .
The Rockwell hardness test method, as defined in ASTM E-18, is the most commonly used hardness test method. You should obtain a copy of this standard, read and understand the standard completely before attempting a Rockwell test.The Rockwell hardness test method is a simple process that uses a diamond cone with a round tip for harder materials and a hardened steel ball indenter for softer ones. With every test, two loads are applied to the test subject. Definition of a Rockwell Hardness Test. The Rockwell test measuring the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load compared to the penetration made by a preload. Hardness is defined as a material’s .
In the Rockwell hardness test, an indenter is pressed into the material to be tested. The indentation depth serves as a measure of the hardness! The measuring process of the Rockwell test is carried out in three .The Rockwell hardness test measures hardness in progressive numbers on different scales corresponding to the size of ball indentor used; scale symbols correspond to the loads of 60 . The Rockwell hardness test is the industry standard measuring system used to determine how resistant a material is to another object. Hardness is defined as a material’s resistance to permanent indentation.High Rockwell hardness numbers represent hard materials and low numbers soft materials. d 2 www.wilsoninstruments.com Fundamentals of Rockwell Hardness Testing Like the Brinell, Vickers, Knoop, Scleroscope and Leeb tests - all of which fall in the general category of indentation hardness tests - the Rockwell test is a measure of the
The Vickers hardness test method was developed by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers hardness test method can .Rockwell hardness test using Rockwell hardness scale is one of the extensively used and accurate hardness test methods prevalent in industries for thin steel, lead, brass, zinc, aluminum, cemented carbides, iron, titanium, . What Does Rockwell Hardness Test Mean? The Rockwell hardness test is the most employed hardness test method. It is used on all kinds of metals, except in situations where the surface conditions and metal structure would produce high variations. This test takes measurements of the permanent depth indentation caused by a load or force on a .
Brinell and Rockwell Hardness Conversion Chart - These Conversion Tables presents data in the Rockwell A, B, C, D, E and F hardness range on the relationship among . The equation for the Rockwell hardness test for metals is below: d=depth from zero load point. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. Rockwell A scale. Used to test: Tungsten carbide. Rockwell B Scale. Used to test: aluminum, brass, and softer steels. Rockwell C Scale. Used to test: harder steels.
⑵Rockwell hardness (HR) When HB>450 or the sample is too small, the Brinell hardness test cannot be used and the Rockwell hardness measurement can be used instead. It uses a diamond cone with an apex angle of 120° or a steel ball with a diameter of 1.59 and 3.18mm, which is pressed into the surface of the material to be tested under a .Modern steels of powder metallurgy rank highest on the Rockwell scale and boast hardness around 64 and 68 HRC. These steels are rare (and hence, more expensive) and harder to process, but, when used correctly, they ensure unbelievable and long-lasting sharpness. . especially suitable for cutlery steels. Vickers hardness test (HV) A pyramidal .Hardness Methods: The Rockwell hardness test measures the depth of penetra-tion of an indenter into a material under a known load. It provides a hardness value based on the depth of penetration. Rockwell Hardness The Brinell hardness test involves indenting a material with a hard sphere under a specific load. Two diameters (x and y 3. Rockwell hardness uses the depth of indentation plastic deformation to determine the hardness value index. A unit of hardness is 0.002 millimeters. When HB>450 or the specimen is too small, the Brinell hardness test cannot be used and the Rockwell hardness measurement is adopted instead.
Common indentation hardness scales are Brinell, Rockwell and Vickers. See also: Hardness. Rockwell Hardness Number – Rockwell Scale. Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an .Applications of Rockwell Hardness Test. Quality Control: Commonly applied in industries that require hard materials on parts and other manufactured products. Material Selection: This tool supports the process of identifying materials that will be applicable depending on the hardness needed. Heat Treatment Evaluation: Using the assessment of the hardness of the treated .
The Rockwell hardness test method has a whopping 30 hardness scales defined by the indenter and the two loads. A Rockwell hardness value is a combination of the numerical hardness number and the Rockwell hardness scale letters preceded by letters HR. For example, a hardness value of 70 on Rockwell scale A is written 70 HRA.Rockwell hardness test measures the permanent depth of indentation on the material by applying a fixed load using an indenter. The smaller the indentation value, the harder is the material. The Rockwell hardness test follows the principle of the differential-depth method. Here, the indenter makes a residual depth called the indent and it is . Rockwell hardness test, a type of hardness test. Hardness Testing Loads. The hardness testing load is the load (“force”) that is applied to the indenter when pressing into the material being tested. The depth or size of .Indenters in a Rockwell hardness test are either hardened steel balls or a conical diamond. Two sets of loads cause an impact on the material surface, which include an initial minor load and a final major load. Additionally, the impact often causes an indentation on the material surface, and measuring the depth of this indentation helps to .
The Rockwell Hardness Test is actually one of several tests aimed to gauge a material’s compatibility as a component to an object based on their strength and durability. The other tests in the series include the the .Proposed by Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell in 1900, it was the first widely used and standardised hardness test in engineering and metallurgy.The large size of indentation and possible damage to test-piece limits its usefulness. However, it also had the useful feature that the hardness value divided by two gave the approximate UTS in ksi for steels.
The Rockwell scale was cocreated by Hugh and Stanley Rockwell in the early 20th century to test the hardness of different materials. There are several different scales by which a material’s hardness is measured on, but blade steels are measured on the C scale. (HRC means Hardness on Rockwell scale C.)The figure below, from Mitsubishi Chemical Advanced Materials, shows the Rockwell hardness test geometry. ASTM D785: A specimen of at least 1/4 inches (6.4 mm) thickness is indented by a steel ball. A small load is applied, the apparatus is zeroed, and then a larger load is applied and removed. After a short time with the preload still applied . Fig. 3-17 Schematic Diagram of the Principle and Test Process of Rockwell Hardness Test (a) Add preload (b) Add main load (c) Unload main load. Hardness symbol: Head used: Total test force N . Have you ever wondered what those mysterious numbers on a metal part mean? In this blog post, we'll dive into the fascinating world of hardness testing .
Hardness Conversion for Rockwell C Scale or High Hardness Range . Regular Rockwell Testing. In this test method, the minor (preload) is always 10 kgf. The major load may be any of the following loads: 60 kgf, 100 kgf, or 150 kgf. Superficial Rockwell Testing. For example, a load of 10 kgf means a force equivalent to 10 kilograms is applied. Steel Hardening Explained Hardness Testing Conversion Table. . The Rockwell hardness test is a widely used method for determining material hardness, especially in high-volume testing environments, due to its speed, simplicity, and efficiency. .
Rockwell Hardness Test. Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). The Rockwell hardness test continues to be applied as a tool for assessing the properites of a product while the tolerances on the acceptable material hardness have become tighter and tighter. Adhering to good practice procedures when performing Rockwell hardness measurements and calibrations is a beneficial step to reducing measurement errors.
Brinell Hardness Test: Rockwell Hardness Test: In Brinell Hardness Test the indenter is a spherical Tungsten Carbide Ball: For the Rockwell Hardness Test, the Indenter is a Small Steel Ball (HRB) or a diamond cone (HRC) Hardness greater than 650 HB can not be measured with the Brinell Scale setup. There is no such limitation in Rockwell .
Variants on the Rockwell hardness test procedure are used depending on the material and strength of a part. The most common Rockwell variants include: HRC – Known as “Rockwell C,” a 150 kgf load is applied via a diamond in this method.
There's a huge demand for a website that helps connect you to people in a platonic way; current random chat platforms aren't working. They're full of bots and often poorly maintained. Emerald wants to change that by offering our users a proper platform to meet and chat to people. Whether its just friends you're looking for or something more.
rockwell hardness test means|rockwell hardness test explained